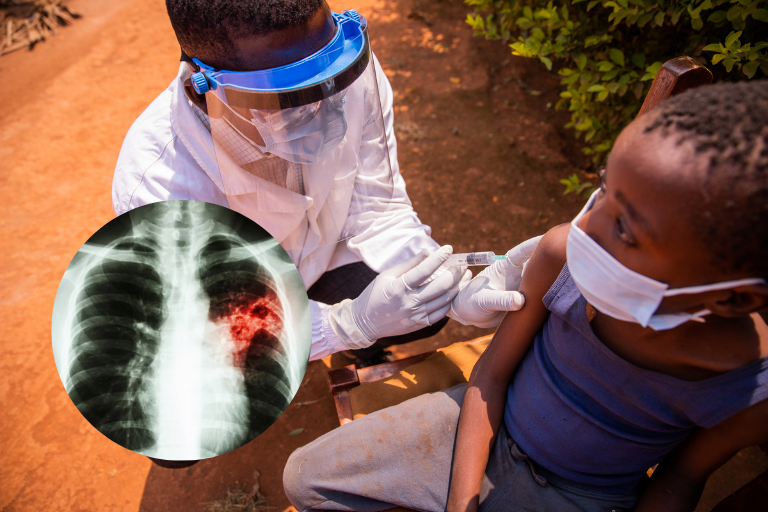
Leprosy and tuberculosis are two of the oldest and most common mycobacterial infections caused by gram-positive aerobic acid-fast bacilli (AFB), Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatous for leprosy and Mycobacterium tuberculosis for tuberculosis. Leprosy involves mostly the skin and peripheral nerves, while tuberculosis is a multisystem disease that primarily affects the lungs but can also involve extrapulmonary sites. Dual infections have been known since ancient times and were first reported in 1954 by Relvich et al.
Current Situation
The Ugandan Ministry of Health has launched comprehensive reviews to assess the current landscape of TB and leprosy within the country. Tuberculosis, which continues to be a leading infectious disease globally, poses a significant threat, particularly in regions with limited healthcare access. Similarly, leprosy, though less prevalent, still requires focused attention due to misconceptions surrounding its transmission and treatment.
Health System Strengthening
Uganda has formed several key partnerships with international bodies to strengthen its health system. Notably, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides technical assistance, guidelines, and resources for disease prevention and control, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), the World Bank, Global Fund, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance
These partnerships enhance Uganda’s health sector by providing funding, training, and technical expertise, contributing to improved health outcomes.
Debunking Myths
Despite significant progress, misinformation remains a barrier to effective treatment and prevention. Common myths surrounding leprosy and tuberculosis hinder public understanding and engagement.
Myth 1: Leprosy is a highly contagious and incurable disease.
Fact: Leprosy is not highly contagious. It is primarily transmitted through prolonged close contact with an infected person. With proper medication, leprosy can be effectively treated, and early diagnosis is key to preventing disability.
Myth 2: Tuberculosis only affects older adults.
Fact: Tuberculosis can affect individuals of any age. Factors such as overcrowded living conditions, inadequate nutrition, and lack of access to medical care contribute to its spread.
According to Daily Monitor, Jennifer Okalany a nursing officer with the TB ward at Mulago referral hospital says that tuberculosis is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis and one can get it from breathing the air from a person suffering from it which can then be transmitted from crowded places like prisons, buses and hospitals.